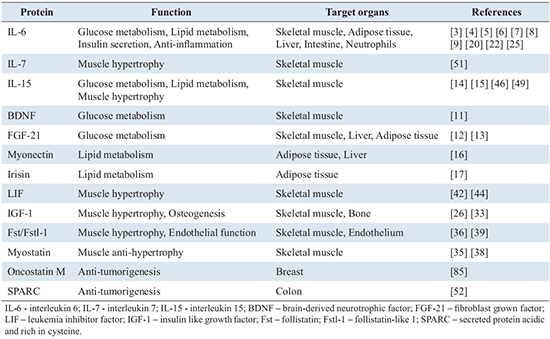
Skeletal muscle secretes several bioactive proteins from within the cell into extracellular fluid. The secretion of several proteins, whose levels increase in response to exercise, can mediate exercise-induced benefits such as metabolic improvement, anti-inflammation, and muscle hypertrophy. We recently found a novel muscle-secreted protein SPARC which may be fundamental for the colon cancer prevention mechanism of regular exercise, demonstrated by various epidemiological studies. Many other proteins, along with c-miRNAs in exosome and metabolites, secreted from muscle have yet to be identified. In the future, the presence and beneficial function of more unknown bioactive factors are expected to be discovered, which strengthens the development of sports science.
Source: BioDiscovery Skeletal muscle: novel and intriguing characteristics as a secretory organ